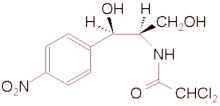
Chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol (or 2,2-dichlor-N-acetamide) is an antibiotic that was derived from the bacterium Streptomyces venezuelae and is now produced synthetically. Chloramphenicol is effective against a wide variety of microorganisms, but due to serious side-effects (e.g., damage to the bone marrow, including aplastic anemia) in humans, it is usually reserved for the treatment of serious and life-threatening infections (e.g., typhoid fever). more...
Regardless of serious side-effects, the WHO advocates its use in many third world countries for pediatric treatment in the absence of cheaper alternatives. It is used in treatment of cholera, as it destroys the vibrios and decreases the diarrhea. It is effective against tetracycline-resistant vibrios.
It is also used in eye drops or ointment, commonly sold under the name of Chlorsig, to treat bacterial conjunctivitis.
Mechanism and Resistance
Chloramphenicol stops bacterial growth by binding to the bacterial ribosome (blocking peptidyl transferase) and inhibiting protein synthesis.
Resistance to chloramphenicol is conferred by the cat-gene. This gene codes for an enzyme called "chloramphenicol acetyltransferase" which inactivates chloramphenicol by covalently linking one or two acetyl groups, derived from acetyl-S-coenzyme A, to the hydroxyl groups on the chloramphenicol. The acetylation prevents chloramphenicol from binding to the ribosome.
Codes
It has many different codings in the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System:
- D06AX02
- D10AF03
- G01AA05
- J01BA01
- S01AA01
- S02AA01
- S03AA08
Read more at Wikipedia.org