METHOD OF PREPARATION
1. Calculate the required quantity of each ingredient for the total amount to be prepared.
2. Accurately weigh and/or measure each ingredient.
3. Mix the acyclovir and chlorhexidine diacetate with 5 mL of propylene glycol to form a smooth paste.
4. Mix the methylparaben and propylparaben with 5 mL of propylene glycol. To this mixture, add the methylcellulose and mix well.
5. Add the methylcellulose-parabens-propylene glycol to 50 mL of the purified water previously heated to about 70°C.
6. After dispersing the mixture in the water, remove from heat and add the acyclovir and chlorhexidine in propylene glycol mixture and about 40 mL of cold purified water and mix well.
7. Add sufficient purified water to volume and mix well.
8. Package and label.
PACKAGING
Package in tight, light-resistant containers.1
LABELING
Keep out of reach of children. Use only as directed.
STABILITY
A beyond-use date of 30 days is appropriate for this preparation.1
USE
Acyclovir and chlorhexidine topical gel has been used in the treatment of topical herpes infections.
QUALITY CONTROL
Quality-control assessment can include theoretical weight compared to actual weight, pH, specific gravity, active drug assay, color, clarity, texture-surface, texture-spatula spread, appearance, feel, rheological properties and physical observations.2
DISCUSSION
This formula is a combination, for topical use, of antiviral and antiseptic agents. If packaged in small tubes or in oral syringes with caps, it can be easily applied and the container resealed without contamination.
Acyclovir (C^sub 8^H^sub 11^N^sub 5^O^sub 3^, MW 225.20) is a synthetic purine nucleoside analog used as an antiviral agent. It is used in the treatment of genital herpes, herpes zoster and varicella in immunocompetent individuals. It occurs as a white to off-white, crystalline powder that is slightly soluble in water and insoluble in alcohol.1,3
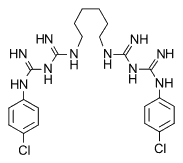
Chlorhexidine diacetate (C^sub 22^H^sub 30^C^sub 12^N^sub 10^.2C^sub 2^H^sub 4^O^sub 2^, MW 625.6) occurs as a white or almost-white, microcrystalline powder that is sparingly soluble in water, soluble in alcohol and slightly soluble in glycerin and propylene glycol. Chlorhexidine is a bisbiguanide antiseptic and disinfectant that is bactericidal or bacteriostatic against a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and is effective against some viruses and fungi.4
Propylene glycol (C^sub 3^H^sub 8^O^sub 2^, MW 76.09) occurs as a clear, colorless, viscous, practically odorless liquid with a sweet taste, somewhat resembling glycerin. It miscible with acetone, 95% ethanol, glycerin and water.5
Methylparaben (C^sub 8^H^sub 8^O^sub 3^, MW 152.15, methyl hydroxybenzoate, methyl parahydroxybenzoate) is available as colorless crystals or as a white, crystalline powder that is odorless, or almost odorless. It is an antimicrobial preservative that is most effective in solutions between pH 4 and pH 8. One gram is soluble in 400 mL of water, 3 mL of 95% ethanol, 60 mL glycerin, 200 mL peanut oil, and 5 mL propylene glycol and it is practically insoluble in mineral oil.6
Propylparaben (C^sub 10^H^sub 12^O^sub 3^, MW 180.20, propyl hydroxybenzoate, propyl parahydroxybenzoate) is available as a white, crystalline, odorless and tasteless powder. It is an antimicrobial preservative that is most effective in solution between pH 4 and pH 8. One gram is soluble in 2500 mL of water, 1.1 mL ethanol and 250 mL glycerin.7
Methycellulose (Methocel) is a practically odorless and tasteless, white to yellowish-white-colored granule or powder that is widely used in both oral and topical formulations. It is used at concentrations of 1-5% in creams, gels and ointments. It is available in different viscosity grades. In cold water, it swells and disperses to form a viscous, colloidal dispersion.8
REFERENCES
1. US Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. United States Pharmacopeia 27-National Formulary 22. Rockville, MD: US Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc.; 2004: 47-48, 2345-2349, 2747.
2. Allen LV Jr. Standard operating procedure for performing physical quality assessment of ointments/creams/gels. IJPC 1998; 2: 308-309.
3. McEvoy GK. AHFS-Drug Information-2004. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; 2004: 765-775.
4. Sweetman SC. MARTINDALE: The Complete Drug Reference. 33rd ed. London: Pharmaceutical Press; 2002: 1138-1140.
5. Weller PJ. Propylene glycol. In: Rowe RC, Sheskey PJ, Weller PJ, ed. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients. 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Association; 2003: 521-523.
6. Reiger MM. Methylparaben. In: Rowe RC, Sheskey PJ, Weller PJ. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients. 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Association; 2003: 390-394.
7. Rieger MM. Propylparaben. In: Kibbe AH, ed. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients. 3rd ed. Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Association; 2000: 450-453.
8. Allen LV, Luner PE. Methylcellulose. In: Rowe RC, Sheskey PJ, Weller PJ. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients. 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Association; 2003: 386-389.
Copyright International Journal of Pharmaceutical Compounding Sep/Oct 2004
Provided by ProQuest Information and Learning Company. All rights Reserved