Chlorpromazine
Chlorpromazine was the first antipsychotic drug, used during the 1950s and 1960s. Used as chlorpromazine hydrochloride and sold under the tradenames Largactil® and Thorazine®, it has sedative, hypotensive and antiemetic properties as well as anticholinergic and antidopaminergic effects. It has also anxiolytic (alleviation of anxiety) properties. Today, chlorpromazine is considered a typical antipsychotic. more...
Chemistry
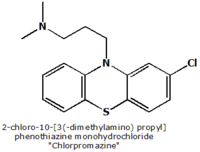
Chlorpromazine is derived from phenothiazine, its chemical name is 2-chloro-10- phenothiazine monohydrochloride and its molecular formula is C17H19ClN2S•HCl. Chlorpromazine has an aliphatic side chain, typical for low to middle potency neuroleptics. The oral bioavailability is estimated to be 30% to 50% due to extensive first pass metabolization in the liver. Its elemination-halflife is 16 to 30 hours. It has many active metabolites (approx. 75 different ones) with greatly varying halflives and own pharmacological profiles. The CYP-450 isoenzymes 1A2 and 2D6 are needed for metabolization of chlorpromazine and the subtype 2D6 is inhibited by chlorpromazine (NB: possible interactions with other drugs).
Mechanism of action
Central
Chlorpromazine acts as an antagonist (blocking agent) on different postsysnaptic receptors -on dopaminergic-receptors (subtypes D1, D2, D3 and D4 - different antipsychotic properties on productive and unproductive symptoms), on serotonergic-receptors (5-HT1 and 5-HT2, with anxiolytic, antidepressive and antiaggressive properties as well as an attenuation of extrapypramidal side-effects, but also leading to weight gain, fall in blood pressure, sedation and ejaculation difficulties), on histaminergic-receptors (H1-receptors, sedation, antiemesis, vertigo, fall in blood pressure and weight gain), alpha1/alpha2-receptors (antisympathomimetic properties, lowering of blood pressure, reflex tachycardia, vertigo, sedation, hypersalivation and incontinence as well as sexual dysfunction, but may also attenuate pseudoparkinsonism - controversial) and finally on muscarinic (cholinergic) M1/M2-receptors (causing anticholinergic symptoms like dry mouth, blurred vision, obstipation, difficulty/inability to urinate, sinus tachycardia, ECG-changes and loss of memory, but the anticholinergic action may attenuate extrapyramidal side-effects).
Additionally, Chlorpromazine is a weak presynaptic inhibitor of Dopamine reuptake, which may lead to (mild) antidepressive and antiparkinsonian effects. This action could also account for psychomotor agitation and amplification of psychosis (very rarely noted in clinical use).
Peripheral
Antagonist to H1-receptors (antiallergic effects), H2-receptors (reduction of forming of gastric juice), M1/M2-receptors (dry mouth, reduction in forming of gastric juice) and some 5-HT receptors (different anti-allergic/gastrointestinal actions).
Because it acts on so many receptors, chlorpromazine is often referred to as 'dirty drug', whereas the atypical neuroleptic amisulpride e.g. acts only on central D2/D3-receptors and is therefore a 'clean drug'. This distinction expresses no valuation of the drugs.
Read more at Wikipedia.org