METHOD OF PREPARATION
Note: This preparation should be prepared in a laminar airflow hood in a cleanroom or via isolation bamer technology by a validated aseptic compounding pharmacist using strict aseptic technique. This is a high-risk preparation.
1. Calculate the required quantity of each ingredient for the total amount to be prepared.
2. Accurately weigh and/or measure each ingredient.
3. Add the ethyl alcohol to about 80 mL of sterile water for injection.
4. Add the lidocaine hydrochloride, ketorolac tromethamine, clonicline and sodium metabisulfite, and mix until dissolved.
5. Add the benzalkonium chloride followed by sufficient sterile water for injection to volume and mix well. (Ten milligrams can be obtained by preparing a 1% aqueous solution, and each 1 mL will contain 10 mg of benzalkonium chloride).
6. Filter through a sterile 0.220 -µm filter into sterile containers.
7. Package and label.
PACKAGING
Package in tight, light-resistant containers.'
LABELING
Keep out of reach of children. Use only as directed.
STABILITY
If not sterility tested: A beyond-use date of up to 24 hours at room temperature, up to 3 days at refrigerated temperature (2 to 8°C), or up to 45 days if frozen can be used for this preparation.1
If sterility tested: A beyond-use date of up to 14 days stored in a refrigerator can be used for this preparation.1
USE
Lidocaine hydrochloride, ketorolac tromethaine and clonidine hydrochloride injection has been used in the treatment of pain.
QUALITY CONTROL
Quality-control assessment can include weight/volume, physical observation, pH, specific gravity, osmolality, assay, color, clarity, particulate matter, sterility and pyrogcnicity.2'3
DISCUSSION
Lidocaine hydrochloride (C^sub 14^H^sub 22^N^sub 2^O.HCL.H^sub 2^O, MW 288.81) occurs as a white, odorless, crystalline powder with a slightly bitter taste. It is very soluble in water (1:0.7) and in alcohol (1:1.5).1'4
Ketorolac tromethamine (C^sub 15^H^sub 13^NO^sub 3^-C^sub 4^H^sub 11^NO^sub 3^, MW 376.40) occurs as a white to off-white, crystalline powder that is freely soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol and dehydrated alcohol. It melts at between InS and 170°C, with decomposition. It should be preserved in tight, light-resistant containers. The pH of a 1 in 100 aqueous solution is between 5.7 and 6.7.1
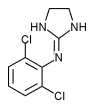
Clonidine hydrochloride (C^sub 9^H^sub 9^Cl^sub 2^N^sub 3^.HCI, MW 260.55) occurs as a white or almost white crystalline powder. It is soluble in water and in dehydrated alcohol. The pH of a 1 in 20 aqueous solution is between 3.5 and 5.S.' Clonidine is an imidazoline antihypertensive that is also used in the prophylaxis of migraine or recurrent vascular headaches, given by continuous epidural infusion in combination with an opioid/ in the treatment of menopausal flushing and in the management of severe cancer pain.
Sodium metabisulfite (Na^sub 2^S^sub 2^O^sub 5^, MW 190.1, disodium disulfite) is an antioxidant occurring as colorless, prismatic crystals or as a white to creamy-white crystalline powder that has the odor of sulfur dioxide and an acidic, saline taste. Tt is soluble l g in 1.9 mL of water, is slightly soluble in 95% ethanol and is freely soluble in glycerin.''
Alcohol (C^sub 2^H^sub 5^OH, MW 46.07, ethyl alcohol, ethanol, grain alcohol) is a clear, colorless mobile and volatile liquid with a slight, characteristic odor and a burning taste. It is miscible with chloroform, glycerin and water 7
Benzalkonium chloride occurs as a white or yellowish-white amorphous powder, a thick gel or gelatinous pieces/flakes with a characteristic mild, aromatic odor, soapy touch and very bitter taste. It is very soluble in water, alcohol and acetone.8
REFERENCES
1. United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. United States Pharmacopeia 27-NationalFormulary22. Rockville, MD: US Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc.; 2004: 487, 1058-1059,2345-2349,2768.
2. Alien LV Jr. Standard operating procedure for particulate testing for sterile products. /JPC1998; 2(1): 78.
3. Alien LV Jr. Standard operating procedure: Quality assessment for injectable solutions./JPC1999; 3(5): 406-407.
4. McEvoy GK. AHFS Drug Information-2004. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; 2004: 3109-3110.
5. Sweetman SC, ed. MARTINDALE: The Complete Drug Reference. 33rd ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press; 2003: 860-863.
6. Stewart JT. Sodium metabisulfite. In: Kibbe AH, ed. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients. 3rd ed. Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Association; 2000: 490-492.
7. Owen SC. Alcohol. In: Rowe RC, Sheskey PJ, Weller PJ, eds. Handbook of Pharmaceutics! Excipients. 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Association; 2003:13-15.
8. Kibbe AH. Benzalkonium chloride. In: Rowe RC, Sheskey PJ, Weller PJ, eds. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients. 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Association; 2003: 45-47.
Copyright International Journal of Pharmaceutical Compounding Jan/Feb 2005
Provided by ProQuest Information and Learning Company. All rights Reserved