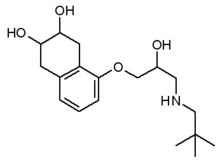
Alpha blockers or alpha-adrenergic blockers
Cardura, Minipress, Hytrin, Doxaloc, Apa-Doxazosin, Gen-Doxazosin, Med-Doxazosin
ACE (angiotensin-Converting Enzyme) Inhibitors
Lotensin, Benicar, Capoten, Vasotec, Monopril, Prinivil, Zestril, Univasc, Aceon, Accupril Altace, Renormax, Mavik
Angiotensin-2-Receptor Antagonists, also known as ARBs
Atacand, Teveten, Avapro, Cozaar, Micardis, Diovan
Beta Blockers (Beta-Adrenergic-Blocking Drugs)
Sectral, Atenolol, Tenormin, Kerlone, Zebeta, Ziac, Cartrol, Coreg, Normodyne, Trandate, Lopressor, Corgard, Levatol, Visken, Inderal, Blocadren
Calcium Blockers or Calcium-Channel-Blocking Drugs
Norvasc, Vascor, Cardizem, Tiazac, Plendil, DynaCirc, Cardene, Adalat CC, Procardia XL, Nimotop, Sular, Calan, Isoptin, Verelan
Thiazide Diuretics
Naturetin, Aquatag, Exna, Marazide, Diuril, Anhydron, Esidrix, HydroDiuril, Diucardin, Saluron, Enduron, Aquatensen, Renese, Metahydrin, Naqua
COPYRIGHT 2005 Center for Medical Consumers, Inc.
COPYRIGHT 2005 Gale Group